The healthcare industry is on the verge of a significant transformation as we approach 2024: transitioning from ICD-10 to ICD-11. Healthcare providers, payers, and patients alike will all be impacted by this shift, which promises to revolutionize the way medical diagnoses and treatments are documented and reported.
Our comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of ICD-11, explores the reasons behind this significant change, and provides actionable strategies to help healthcare organizations prepare for it.
Understanding ICD-11 Transition Guide: What’s New?
The World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases, 11th Revision (ICD-11), is the latest update to the global diagnostic classification system. ICD-11 replaces ICD-10, which has been in use for more than two decades. The ICD-11 is intended to enhance the accuracy, reliability, and usability of health information and reflect the complexity of modern medicine. An ICD-11 Transition Guide will be invaluable for healthcare professionals to effectively adapt to these updates and ensure accurate coding in clinical documentation.
Key Features of ICD-11:
-
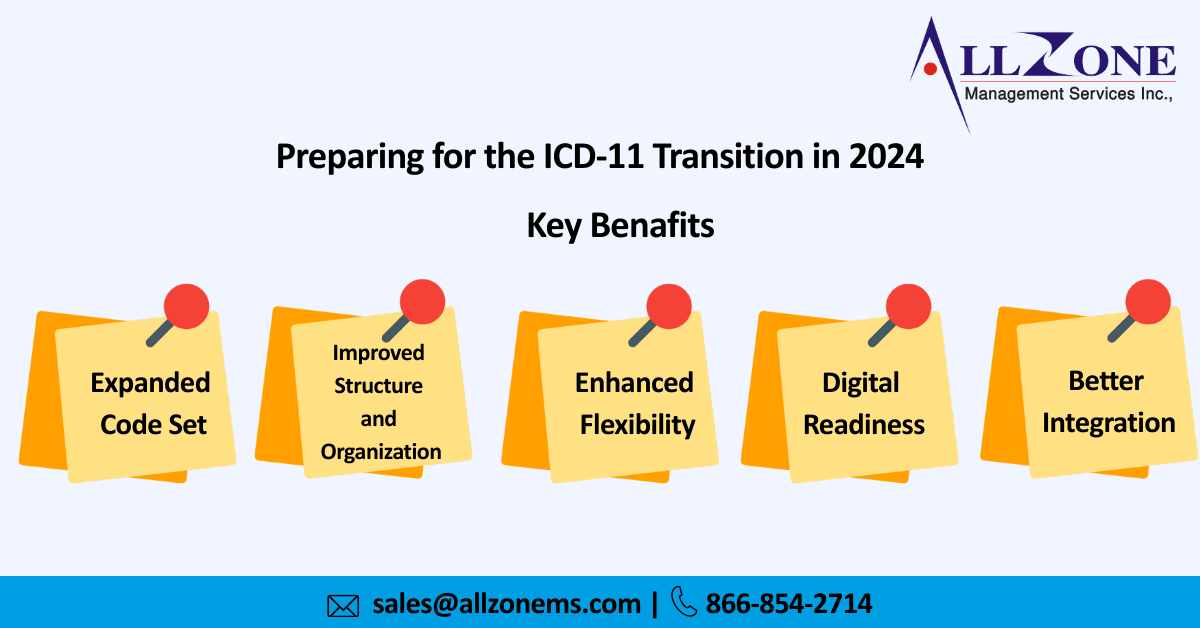
- Expanded Code Set: As a result of the addition of more detailed and specific diagnostic codes in ICD-11, patient conditions can be more precisely documented and treatments can be analyzed more precisely.
- Improved Structure and Organization: A new system uses a more intuitive, user-friendly structure that organizes diseases and conditions based on their underlying causes and pathophysiology to make navigation simpler for healthcare providers.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Health systems and practices use ICD-11, which is designed to be flexible enough to fit a variety of contexts and settings. IT supports a broad range of health systems and practices to meet local requirements.
- Digital Readiness: A key component of ICD-11 is its support for electronic health records (EHRs) and other digital health systems so that seamless integration and cross-platform data exchange are possible.
- Better Integration with Other Classification Systems: This system is designed to be more aligned with other classification systems, including the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) and the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O).
The Rationale behind the Transition
The transition to ICD-11 is driven by several key factors:
-
- Advancements in Medical Knowledge: During the past decade, medical science has advanced significantly, and ICD-11 provides a more up-to-date and accurate representation of health conditions by incorporating new research and clinical insights.
- Global Standardization: In addition to improving global health data consistency and comparability, ICD-11 facilitates more efficient health policy development, research, and monitoring across different countries and regions.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Health outcomes can be improved, health statistics are more accurate, and public health interventions can be more effective through ICD-11’s expanded code set and improved structure.
- Support for Emerging Health Issues: A forward-looking approach ensures that ICD-11 remains relevant in a rapidly changing healthcare environment by accommodating emerging health issues and diseases, including mental health, digital health, and new infectious diseases.
Preparing for the ICD-11 Transition: Key Considerations
ICD-11 transition is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations to help healthcare organizations prepare:
Education and Training
-
- Staff Training: Educate all relevant employees, including physicians, coders, billers, and other healthcare professionals, about ICD-11 during the preparation process.
- Training Programs: Training programs about ICD-11 coding and documentation practices should provide comprehensive instruction. Online courses, workshops, and webinars are among the best ways to reach a wide audience.
- Resource Materials: Resources such as manuals, quick reference guides, and online tools should be provided to staff to assist them with the transition. Make sure these resources are regularly updated and easy to find.
Systems and Technology
-
- EHR Integration: Consult your EHR vendor to ensure the system can support ICD-11 codes and workflows. Determine your current EHR’s compatibility with ICD-11.
- Software Updates: In order to accommodate ICD-11, necessary software upgrades and modifications may have to be implemented. This may include software updates for coding, medical billing, and other health information systems.
- Testing and Validation: It is imperative that you test your systems thoroughly to ensure that they accurately handle ICD-11 codes and workflows. If there are any errors, address them before the new system is launched.
Medical Coding and Documentation
- Code Mapping: Develop a plan to map ICD-10 codes to their ICD-11 counterparts, including identifying equivalent codes and determining how to move from one system to the other.
- Documentation Practices: ICD-11 documentation practices should be reviewed and updated in accordance with ICD-11 requirements. Clinical documentation should include details necessary to support accurate ICD-11 coding.
- Audit and Compliance: It is important to implement audit procedures to ensure accuracy of coding and compliance with ICD-11. Regular audits can produce early identification and resolution of any issues during the transition period.
Communication and Coordination
-
- Stakeholder Engagement: Maintain relationships with ICD-11 stakeholders, such as payers, regulatory agencies, and professional associations.
- Internal Communication: Maintain clear communication channels within your organization to keep employees informed about the transition process and any changes to workflows or procedures.
- Patient Communication: Make sure patients understand the benefits of the new system and how the transition to ICD-11 will affect their care.
Financial and Operational Impact
-
- Cost Analysis: Prepare a cost analysis to understand the financial implications of the ICD-11 transition. This should include costs associated with training, system updates, and potential changes to medical billing and reimbursement systems.
- Operational Adjustments: Determine what impact ICD-11 will have on your organization’s operations and workflow. Determine if any adjustments are needed to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
- Reimbursement Considerations: Make sure you understand how payers and insurers will handle ICD-11 coding for reimbursement purposes. Adapt your billing practices accordingly if reimbursement policies change.
Implementing a Transition Plan
ICD-11 transition plans are crucial for a successful switch. Following is a step-by-step guide to developing and implementing yours:
Assessment and Planning:
-
- Conduct an Impact Assessment: Consider how ICD-11 will affect your organization’s processes, systems, and staff, and develop an action plan to deal with any issues that arise.
- Create a Transition Team: Develop and maintain a dedicated team for overseeing the ICD-11 transition, including representatives from IT, billing, coding, and clinical services.
- Develop a Timeline: Prepare a realistic transition timeline, including key milestones and deadlines. Make sure there is enough time for training, system upgrades, and testing.
Training and Education:
-
- Roll out Training Programs: Ensure that training programs are implemented for all employees participating in the transition. Provide ongoing support and resources to assist them in adapting to the new system.
- Monitor Progress: Provide additional support if needed to ensure that all staff are prepared for the transition. Track the progress of staff training and address any issues, challenges, or delays that occur.
System Updates and Testing:
-
- Update Systems: Make sure that all necessary changes are made before the transition date that support ICD-11. Compile a list of what needs to be updated. Work with your IT team and vendors to update systems and software to support ICD-11.
- Conduct Testing: Testing your systems thoroughly will ensure that they accurately handle ICD-11 codes and workflows. Address any issues or discrepancies that are identified during testing.
Go-Live and Monitoring:
-
- Go-Live: The implementation of ICD-11 should take place at the scheduled go-live date. All systems and processes should be fully operational and staff should be prepared to deal with any issues that may arise.
- Monitor and Support: Make sure that you are providing ongoing support and monitoring during the initial implementation period. Address any issues as soon as possible and adjust as necessary in order to facilitate a smooth transition.
Evaluation and Optimization:
-
- Evaluate Performance: The ICD-11 implementation process is being evaluated to identify any areas for improvement. Staff and stakeholders are being consulted to understand their experiences and challenges.
- Optimize Processes: Enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of ICD-11 coding and documentation by taking the insights gained from the evaluation into account when optimizing processes and workflows.
ICD-11 Transition Guide: Enhancing Patient Care and Health Information Quality
Data classification and reporting in healthcare have undergone a significant change since ICD-11 was introduced. Healthcare organizations can navigate this change effectively and position themselves for success in the evolving healthcare landscape by understanding the key features of ICD-11, the rationale behind the transition, and the steps required to prepare. An ICD-11 Transition Guide will serve as a crucial resource in this process, offering detailed insights to support the shift.
An ICD-11 preparation program involves a comprehensive approach, including training and education, system updates, medical coding and documentation adjustments, communication and coordination, as well as financial and operational considerations. Healthcare organizations can ensure a smooth and successful transition to ICD-11 by developing a detailed transition plan and implementing it thoughtfully, resulting in improved patient care and enhanced quality of health information.
ICD-11 offers a number of opportunities to advance healthcare delivery and achieve modern medicine’s goals as we move forward into 2024. In an increasingly complex and dynamic healthcare environment, healthcare professionals can navigate this transition with confidence and continue to provide high-quality care by staying informed and proactive, guided by a well-structured ICD-11 Transition Guide.